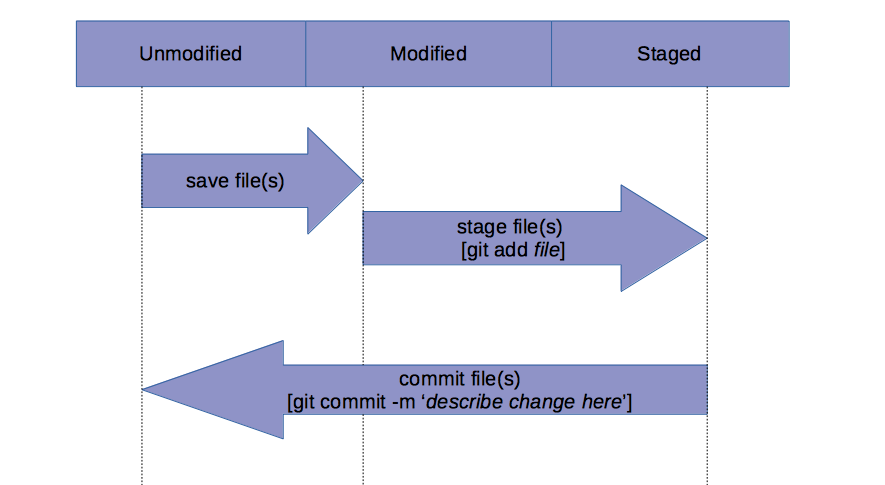
To utilize these commands, be sure you are in the directory of the repository you intent to work on by typing cd directory_name from your home directory.
git initstart tracking a directory with git (this only needs to be done once within a directory)git statustracks the current status of your filesgit add <name_of_file.txt>add a file to track (goes to stagin area)git commit -m 'Message about your changes'commit changes (use the message 'Initial commit' for the first commit in a repository)git diff <name_of_file.txt>to see changes since last commit
amyrippeto~$ mkdir favorite_things
amyrippeto~$ cd favorite_things
amyrippeto~/favorite_things$ touch musical_artists.txt
amyrippeto~/favorite_things$ ls
musical_artists.txt
amyrippeto~/favorite_things$ git init
Initialized empty Git repository in /Users/amyrippeto/favorite_things/.git/
amyrippeto~/favorite_things$ git add musical_artists.txt
amyrippeto~/favorite_things$ git status
On branch master
No commits yet
Changes to be committed:
(use "git rm --cached <file>..." to unstage)
new file: musical_artists.txt
amyrippeto~/favorite_things$ git commit -m 'Initial commit'
[master (root-commit) ccbccff] Initial commit
1 file changed, 0 insertions(+), 0 deletions(-)
create mode 100644 musical_artists.txt
amyrippeto~/favorite_things[master]$ git status
On branch master
nothing to commit, working tree clean
amyrippeto~/favorite_things[master]$ echo "ZZ Ward, Glass Animals, Milky Chance" >> musical_artists.txt
amyrippeto~/favorite_things[master !]$ git status
On branch master
Changes not staged for commit:
(use "git add <file>..." to update what will be committed)
(use "git checkout -- <file>..." to discard changes in working directory)
modified: musical_artists.txt
no changes added to commit (use "git add" and/or "git commit -a")
amyrippeto~/favorite_things[master !]$ git add musical_artists.txt
amyrippeto~/favorite_things[master !]$ git status
On branch master
Changes to be committed:
(use "git reset HEAD <file>..." to unstage)
modified: musical_artists.txt
amyrippeto~/favorite_things[master !]$ git commit -m 'Add 3 artists'
[master a6e9772] Add 3 artists
1 file changed, 1 insertion(+)
amyrippeto~/favorite_things[master]$ git status
On branch master
nothing to commit, working tree clean
amyrippeto~/favorite_things[master]$ cat musical_artists.txt
ZZ Ward, Glass Animals, Milky Chance
amyrippeto~/favorite_things[master]$
- In your terminal command line
cdto the directory you want to work on. - Once in the directory type name of your text editor followed by a space then a period to open the file in your text editor. to use Atom you would type
atom . - This will open the directory in your text editor. You can now select the file you want to make changes to and do so in the editor.
- Once you are satified with your changes, save them by using the shortcut command + s
- Return to your terminal (use shortcut command + tab)
- Type
git add name_of_file_changed.txtto add to the staging area. - Type
git statusto confirm the file has been modified and staged. - Now you can commit the changes by typing
git commit -m 'Add specified changes'(use your own message) - To view the changes to the file you can type
git diff name_of_file_changed.txtin the command line
Note: There is so much more that can be accomplished using Git. Hopefully these basics help you get started!