- Hands on, thus no slides
- This should bring you through your first 1-2 years definitely
- The absolute minimum of theory
- Get started FAST (alone):
- New Project
- Existing Project
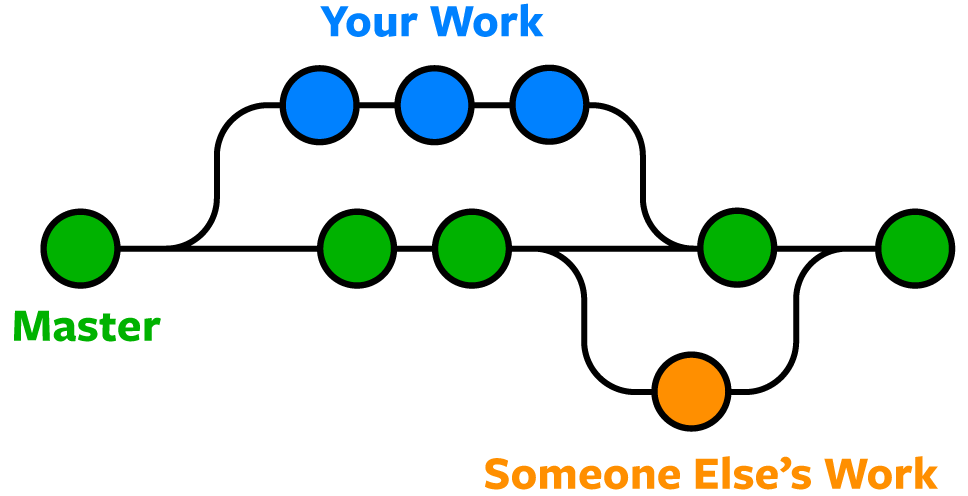
- Work with others
- You are part of the project
- Public project
- Fancy Pants Features
- Where to find more
-
What is it
- Distributed Version Control System
- Tracks named changes to your code over time
- Used to collaboratively work together on code
-
Why is it needed?
- Keep history of all changes (with explainations)
- Allows collaboration using "branches"
- Allows for easy reverts and comparisons
-
How does it work
- A directed tree of named updates
- Each git can be thought of a bunch of diffs with a name
- The named updates form a usually linear history
- The history can break up (branch), and then be put together again (merge)
-
Needed Lingo:
- Repository: Central place for a project.
- Internally, a magic
.gitfolder within the projects root
- Internally, a magic
- Commit: A named update, representing a snapshot at a specific point in time
- Each commit has one or more parents, which point to the previous commits
- This snapshot can be viewed again, called a checkout
- Branch: Lightweight, movable pointer showing the newest commit of a given graph branch
- Represent one independent line of development
- Repository: Central place for a project.
- Git != GitHub != GitLab
- Git: The Open Source Software itself
- GitHub/GitLab/Codeberg/...: Web-based platforms to host git repositories
- Load git
git --version
module av
module load git
git --version- Create SSH key if you don't have already
ssh-keygen -t ed25519 -C "[email protected]"
cat .ssh/id_ed25519.pub- Upload SSH Key to GWDG GitLab
- Link to our GitLab
- Disable "Initialize repository with a README"
git init # Only creates .git
git config --global user.name "John Doe"
git config --global user.email "[email protected]"
git config --global core.editor "vim"
# TODO: Show where its stored (global/local)
git remote add origin ... # Origin is only convention => Decentralized
# edit stuff
git status # untracked/staged/committed
git add
git commit
git status
git log
git push --set-upstream origin master
# show in webgit status
# edit stuff
git status
git diff
git add
git diff
git diff --staged
git commit
git status
git diff
git diff --staged
git log
git push # no --set-upstream origin master
git remote -v
cat .git/configgit log
git log --oneline
git --no-pager log --oneline# edit stuff
git config --local user.name "Aztec Pwn3r"
git config --local user.email "[email protected]"
git commit -am "I catn spel"
git pushOH NO!!
git config --unset --local user.email
git config --list
git commit --amend --no-edit
git log -1Half way there: Commit still wrong!
git commit --amendUpdate remote:
git push
# The following is a really really bad idea...
git push --force
# Settings -> Repository -> Protected Branchescd ..
rm -rf
module list
git clone # Use SSH, not HTTP
git status
git log --oneline
# ...another commit
git clone
cd
git status
git log --oneline -10
# ..add another commitgit status # We should be on master
echo "\nwritten on master" >> README.md
git add .
git commit
git log --oneline --graph --all
git switch -c notmaster
git status
echo "\nwritten on notmaster" >> README.md
git add .
git commit
git log --oneline --graph --allgit status
git switch master
git merge notmaster
# ...fixIf you screwed up: git merge --abort and try again
- Pull master/main to be up2date
- Branch out for a new feature (maybe encode issue digit)
- Work on feature
- Open Merge Request onto master/main
- (Manual) Review Process
- Feature on master/main :)
Goal: Know that they exist
- Can be anywhere in git repo (not only root)
- Example:
exact_match.txt
node_modules/ # i.e. a directory
/just_in_this_folder.txt
*.secret
- Usually never used in terminal
- See web interface
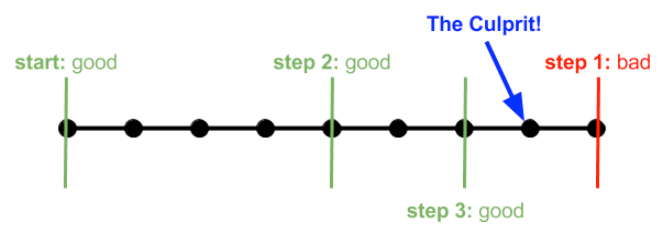
git bisect start
git bisect bad
git bisect good <good-commitish> # for example, tags or branch (as their heads) are also okay
Then iteratively
git bisect good # or
git bisect bad
At the end
git bisect reset
git bisect start
git bisect bad
git bisect good <good-commitish>
git bisect run ./test_script.sh
- Problem: You want to pull but have stuff uncommitted (but tracked)
- Solution:
git stash(a stack for temporary data)
git stash
git pull
git stash pop
git rm --cached <path>git rm -f <path>git reset --soft HEAD~1git reset --hard HEAD~1git revert <commitish>
-
What we left out
- What you can still learn:
- Forking (for public work)
- merge vs rebase ("forced" forward merge)
- git cherrypick
- git worktrees
- How to really recover your mess with git reflog
- squashing
- What you can still learn:
-
Where you can learn more
- Very recommended: Primagens Free Git Tutorial on Boot.dev
- Reference: Pro Git Book
- Internals: Building Git