-
-
Save seaside2mm/964104add4ea3f1d480b21ca79c1ac8f to your computer and use it in GitHub Desktop.
https://vincentqin.tech/posts/superpoint/ https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/69515306
第一步: 利用基本形状元素渲染得到训练集和真值 用虚拟的三维物体作为数据集,训练网络去提取角点,这里得到的是BaseDetector即,MagicPoint;
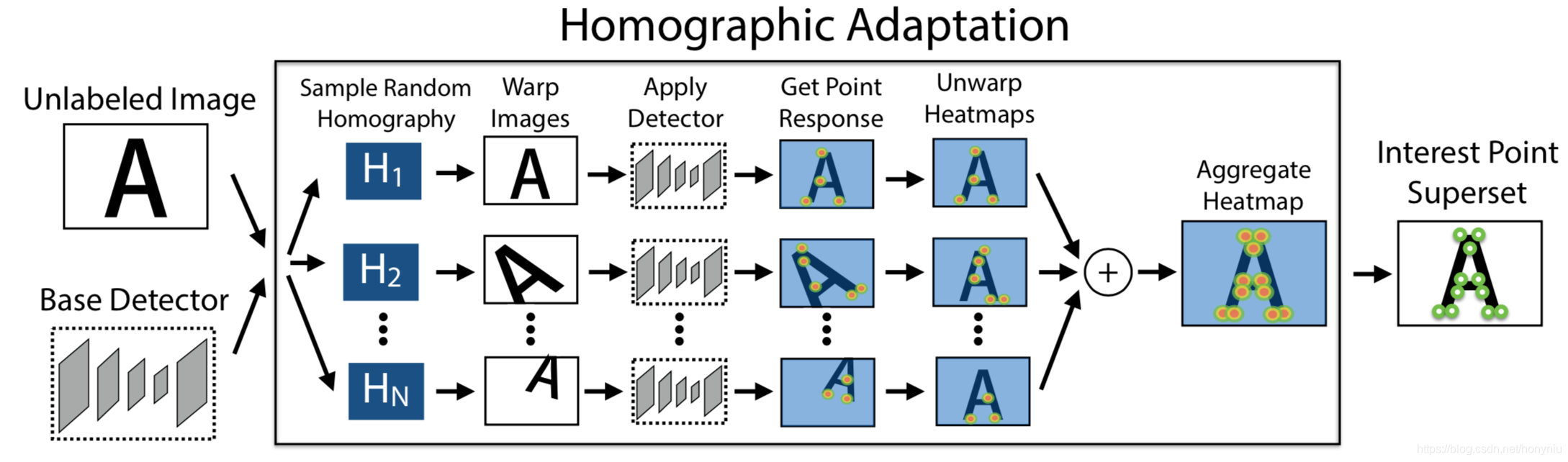
第二步: 兴趣点自标注(Interest Point Self-Labeling) 通过之前训练好的MagicPoint获取数据集的特征点的真值
对每张图像做n种单应变换,得到n张变换后的图像,在这些图像上利用MajicPoint模型分别提取特征点,可以得到n个特征点的heatmap,把这n个heatmap累加到一起,得到最终的heatmap,然后使用阈值截取获得每个位置上的特征点,这个就是原始图像的特征点的真值,用来训练。
第三步: 特征点提取和描述符计算联合训练 同特征点一样,描述符也存在真值的问题,任意两张图像,真值是没法确定和标注的。这里的描述符直接由深度学习网络的feature map输出,但是这样的feature map不一定满足描述符的特性,简单来说就是需要同样的特征点之间描述符的距离尽可能的近,而不同特征点之间的描述符的距离尽可能远。
该文对原始图像做warp,然后两张图像都能特征点对应关系也是知道的,由warp函数决定,对于两张图像中任意的两对点都会求loss,去优化使匹配点距离小,非匹配点距离大,这样最后得到的描述符就是满足需求的。
需要注意的是描述符的feature map是通道为D的,但是分辨率是原始图像的1/8,也就是8x8的图像patch需要公用同一个描述符,描述符的维度是D。
第一步:创建Synthetic Shapes Dataset并训练MagicPoint特征检测器 Synthetic Shapes Dataset是合成形状数据集,该数据集有9种不同的形状(包括椭圆和高斯噪声,作为负样本),并有.npy文件记录特征点的坐标位置作为label进行训练,如下图所示。
python train4.py train_base configs/magicpoint_shapes_pair.yaml magicpoint_synth --eval
- 当第一次训练时,将生成合成形状数据集,数据集保存在
datasets/synthetic_shapes_v6文件夹中。 magicpoint_shapes_pair.yaml文件里面有可修改的各种数据及训练参数。- 训练完成后,权重将保存在
dataset/magic-point_synth/中,里面也包括了Tensorboard的记录文件。
第二步:MagicPoint检测器自标注数据集 得到训练后的MagicPoint检测器后,我们需要使用它对真实图像数据集进行标注,获得伪真实(pseudo-ground truth)的data及label,其中进行了一个图像处理操作叫做Homographic Adaptation,它也是SuperPoint这么好用的一个创新点。当然,你也可以在yaml文件中设置选择开启或关闭该操作。
输出为一堆.npy文件,记录了输入图像的特征点伪真实标签,输出路径在 EXPER_PATH/outputs/magic-point_coco-export1/ 。在npy文件中特征点坐标保存在 属性f.points 。同样,在magicpoint_kitti_export.yaml文件中可以进行各种调参。
# 查看特征点标签(label)的坐标
point_path = 'xxx.npz'
npz = np.load(point_path)
point = npz.f.points.tolist()
print(npz.f.points)- make sure the pretrained model in config file is correct
- make sure COCO dataset is in '$DATA_DIR' (defined in setting.py)
- config
- check the 'root' in config file
- train/ val split_files are included in
datasets/kitti_split/.
#python3 export.py <export task> <config file> <export folder> [--outputImg | output images for visualization (space inefficient)]
python3 export.py export_detector_homoAdapt configs/magicpoint_kitti_export.yaml magicpoint_base_homoAdapt_kitti这一步我们可以选择不用COCO数据集,替换为自己的数据集,但要注意替换的数据集图像尺寸必须要能被8整除。
1.修改训练图像尺寸 2.修改读取图像路径
第三步:再次训练MagicPoint检测器 在第一步训练出来的MagicPoint检测器虽然可以检测出一些特征点,可因为是使用合成形状数据集训练出来的模型,检测性能还有些不足,所以进行第二步自标注数据,再用标记好的真实图像训练,得到的强化版的检测器。 You need pseudo ground truth labels to traing detectors. Labels can be exported from step 2) or downloaded from link. Then, as usual, you need to set config file before training.
- config file
- root: specify your labels root
- root_split_txt: where you put the train.txt/ val.txt split files (no need for COCO, needed for KITTI)
- labels: the exported labels from homography adaptation
- pretrained: specify the pretrained model (you can train from scratch)
- 'eval': turn on the evaluation during training
第四步:Export/ Evaluate the metrics on HPatches
指定yaml文件并设置pretrained model等信息
- 导出keypoints, descriptors, matching
# download HPatches dataset (link above). Put in the $DATA_DIR.
# python3 export.py <export task> <config file> <export folder>
python3 export.py export_descriptor configs/magicpoint_repeatability_heatmap.yaml superpoint_hpatches_test- 评价
Evaluate homography estimation/ repeatability/ matching scores ...
# python evaluation.py <path to npz files>
python evaluation.py logs/superpoint_hpatches_test/predictions --repeatibility --outputImg --homography --plotMatchingpython train4.py <train task> <config file> <export folder> --eval
python train4.py train_joint configs/superpoint_coco_train_heatmap.yaml superpoint_coco --eval --debug
python train4.py train_joint configs/superpoint_kitti_train_heatmap.yaml superpoint_kitti --eval --debug
- set your batch size (originally 1)
- refer to: 'train_tutorial.md'
参数
out_num_points: 输出特征点数patch_size: TODOnms_dist: Distance to suppress, measured as an infinty norm distance.conf_threshto change the point confidence threshold (default: 0.015).nn_threshto change the descriptor matching distance threshold (default: 0.7).
device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
torch.set_default_tensor_type(torch.FloatTensor)
# load config
with open('configs/magicpoint_repeatability_heatmap.yaml', 'r') as f:
config = yaml.load(f)
# load model
Val_model_heatmap = get_module('', config['front_end_model'])
# load pretrained
val_agent = Val_model_heatmap(config['model'], device=device)
val_agent.loadModel()
net = val_agent.net
# load gray image to tensor data
gray_img = Image.open('datasets/KITTI/2011_09_26_drive_0001_sync_02/0000000000.jpg').convert('L')
gray_img_np = np.array(gray_img).astype("float32")
H, W = gray_img_np.shape[0], gray_img_np.shape[1]
img_torch = torch.from_numpy(gray_img_np.reshape(1, 1, H, W))
outs = net(img_torch.to(device))
params = {
'out_num_points': 500,
'patch_size': 5,
'device': device,
'nms_dist': 4,
'conf_thresh': 0.015
}
sp_processer = SuperPointNet_process(**params)
outs_post = net.process_output(sp_processer)
pts_int = outs_post['pts_int']
pts_offset = outs_post['pts_offset']
# pts_desc = outs_post['pts_desc']
img = draw_keypoints(toNumpy(img_torch.squeeze()), toNumpy((pts_int+pts_offset).squeeze()).transpose())
plt.imshow(img.astype(int))
plt.show()