Just jotting down some ideas. Inspired by flexbox, Morphorm, and Figma's autolayout engine.
- This is currently okay on most properties excluding offsets, paddings and margins.
- This would require no usage of absolute directions (top/bottom/left/right).
Pixelsare a unit of length defined by a logical pixel.Percentis a relative unit of length defined by the computed dimensions of an anchor element (usually a parent, although seepositionfor edge cases) excluding padding.
layout will specify the direction in which children are stacked inside of a container.
- Row will stack children horizontally.
- Column will stack children vertically.
Determines how children are aligned in a container.
align_rowscontrols how children are aligned in the Row axis.align_columnscontrols how children are aligned in the Column axis.
position determines how a node will be positioned in the layout. It also defines a node's anchor element, or point of reference.
- Absolute positioning will remove the node from the layout and anchor it based on its
offsetvalues relative to its nearest parent. - Relative positioning (default) will keep the node in the layout tree, and treat
offsetvalues as an offset from its position in the layout. - Fixed positioning is the same as Absolute positioning, but the node is positioned relative to the window, rather than the nearest parent.
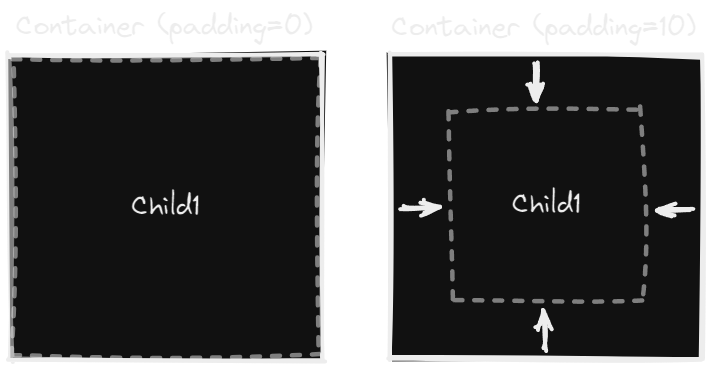
Padding determines the space between a container and its children.
gap specifies the uniform spacing between child elements.
- This is separate from (and should be added to)
margin, which allows each individual child to specify its own spacing on each side. - If
Fillis set, the elements will be spaced evenly over the remaining available space.
margin determines an individual child's spacing from other elements in the layout. This is added to gap, if its set.
- If
Fillis set, the element will be spaced away from other elements using the remaining available space.
If the length of the child elements exceeds the length of the parent on given access, then child elements may be wrapped (rather than overflowing), placing them on the next available line.
gapshould be taken into account when spacing wrapped elements.
These properties will offset a child element from its original position without affecting other elements in the layout.
Determines the dimensions of an element. Fill will fill the remaining available space on an axis, while fit will set the element to its minimum possible width to fit its child contents.
- If multiple children of a row/column have
Filldimensions, then space will be evenly distributed between them. - By default, width/height are both
Fit.
Determines the sizing constraints that an element has. An element cannot get smaller or larger than these values.
- Don't think it makes sense to have
Fillhere due to its dynamic.